Passive Fire Protection Systems for Power Distribution & Storage
World leader in engineered passive fire protection with over 35+ years of performance-driven experience.
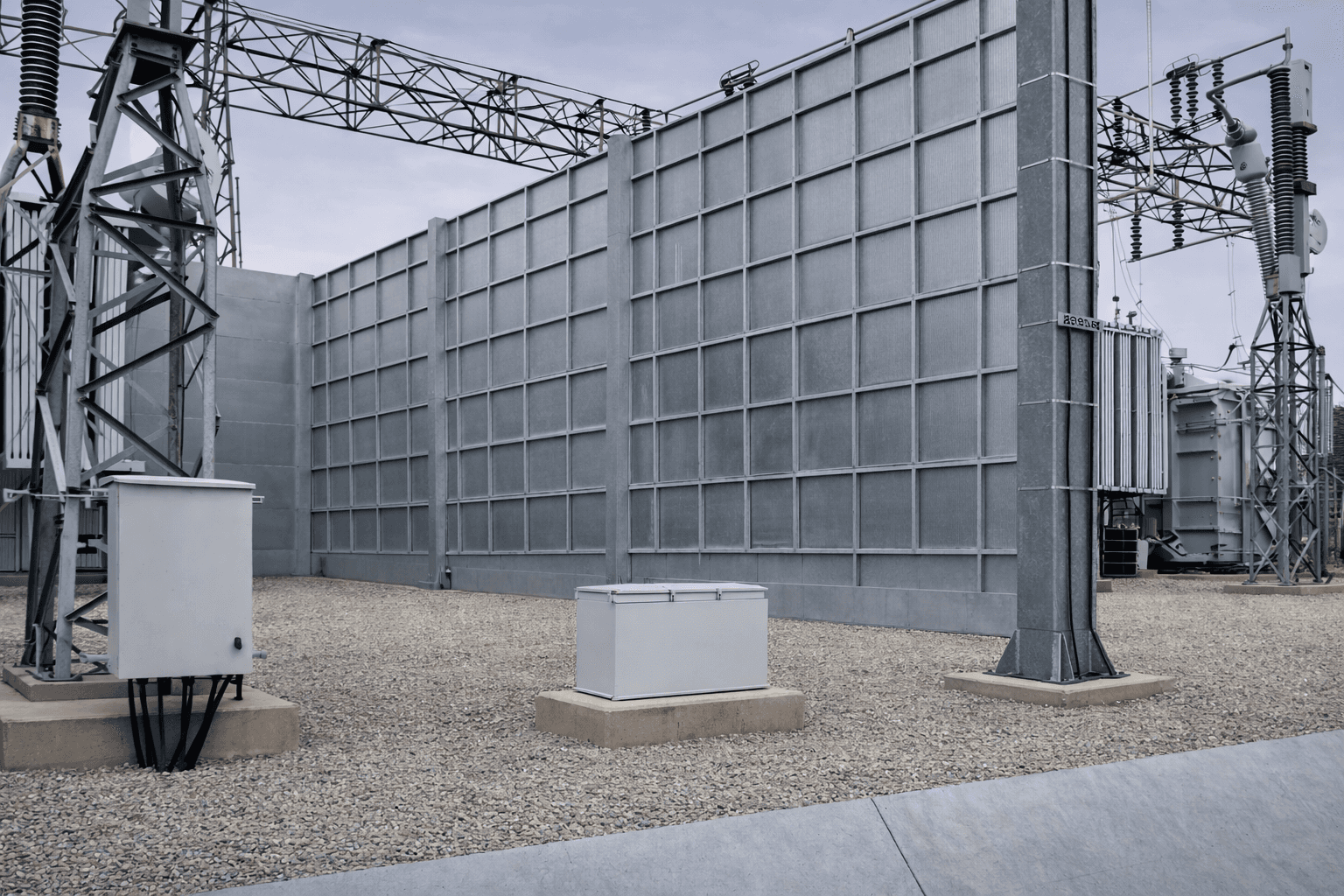
From fire rated barriers and walls to custom enclosures, our systems are engineered to integrate into complex sites with proven performance and long term reliability.

Featured System
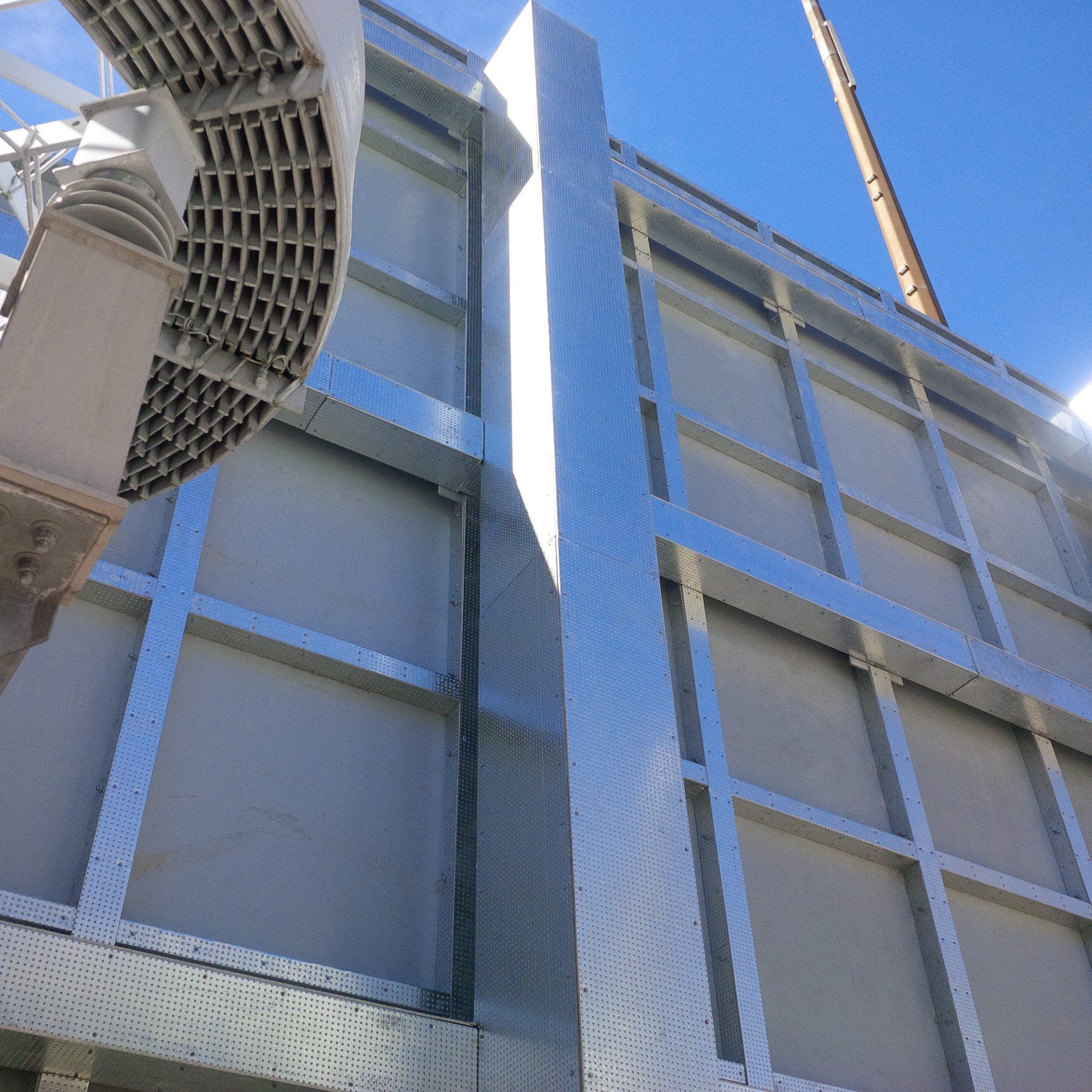
BESSY is a purpose built fire barrier system designed to contain and manage thermal events within Battery Energy Storage Systems while protecting adjacent assets and critical infrastructure. Engineered by DuraSystems, BESSY delivers proven fire protection for high risk energy environments where reliability and safety are essential.
Engineered for Battery Energy Storage
Engineered for long term durability and code compliance, BESSY integrates seamlessly into complex sites while supporting regulatory approval.
Rated Fire Resistance
Available with multi hour fire resistance ratings, BESSY is designed to contain thermal events for extended durations, helping limit escalation and protect surrounding infrastructure.
Our Products
DuraSystems solutions are deployed in environments where safety, reliability, and compliance are critical to the operations they protect.
Passive fire protection for facilities where failure is not an option.
Our solutions are designed for high consequence environments where reliability, performance, and long term durability are essential.
Years in Passive Protection
Power Distribution Installations
Operational Reliability Focus
Where Our Systems Are Used
Passive fire protection across critical industries.

What we focus on
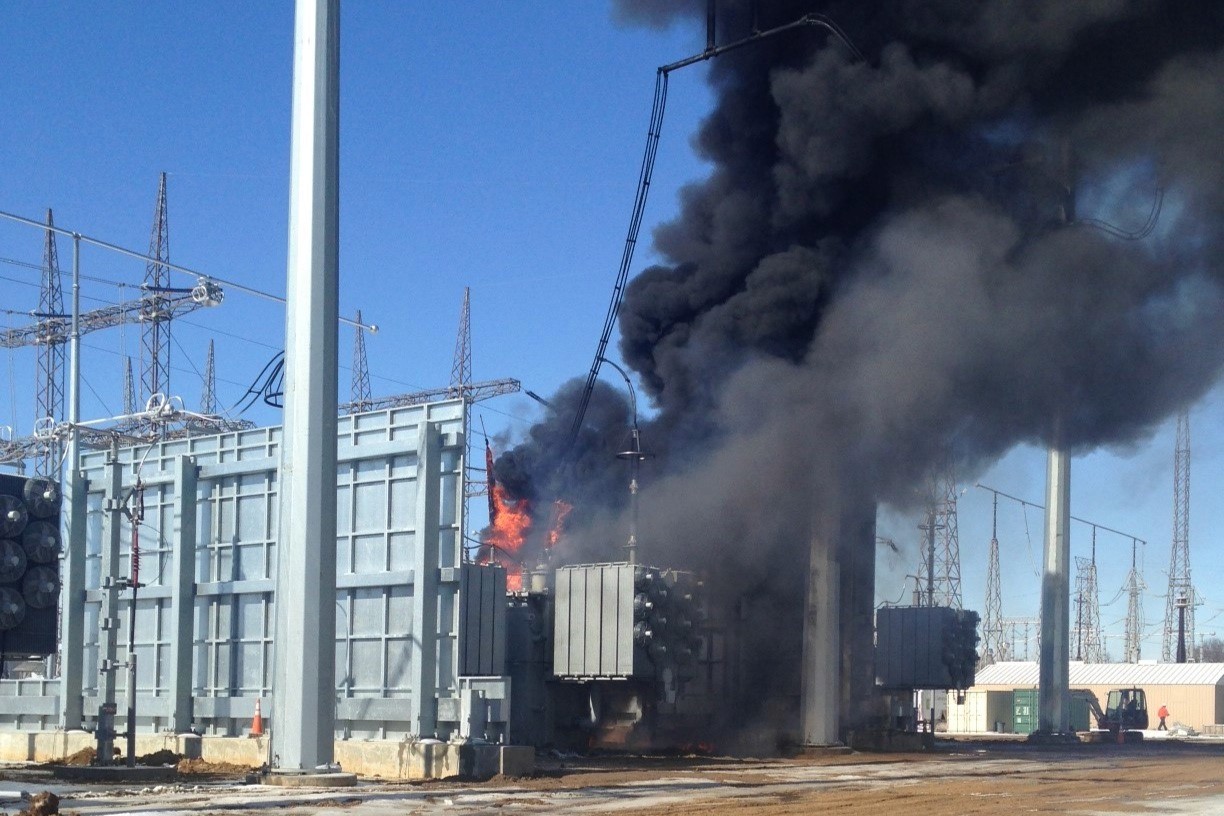
We design passive protection systems that contain extreme fire and blast events, prevent escalation, and support safety and compliance in the world’s most demanding environments.
Engineered Protection
We focus on designing systems that perform under extreme conditions, using tested assemblies and engineered solutions rather than assumptions or shortcuts.
Performance and Compliance
Every system is designed to meet strict fire, blast, and safety standards while integrating efficiently into complex facilities and sites.